
![]()
Search the Journey to Forever website – click HERE
|
Journey to Forever: Make a donation |
Navigation
| Small farms library | |
| City farms | |
| Organic gardening | |
| Composting | |
| Small farms | |
| Introduction Sustainable farming Small farms fit References |
|
| Small farm resources | |
| Back to the land | |
| Small farms | |
| Organics | |
| Soil management | |
| Sustainable farming | |
| General resources | |
| Food storage and preservation | |
| Useful databases | |
| Community-supported farms | |
| Farming with trees | |
| Agroforestry Bamboo Resources |
|
| Farming with animals | |
| Introduction Livestock resources Cattle Sheep General Draft animals |
|
| Pasture | |
| Introduction Pasture resources Silage |
|
| Pigs for small farms | |
| Why pigs have snouts Raising pigs on soil in Japan Lady Eve's pigs Pigs on pasture Pig resources |
|
| Poultry for small farms | |
| Muscovy ducks Khaki Campbell ducks Chickens Geese Rabbits Guineafowl General tips High-protein poultry feed from thin air Poultry as unpaid labour They're not pets Doing it |
|
| Poultry resources | |
| Aquaculture for small farms | |
| Introduction Aquaculture resources |
|
| Composting for small farms | |
| Foundation On-farm composting resources |
|
| Controlling weeds and pests | |
| Weeds Weed control resources Insect pests No pesticides Insect control resources |
|
Contact usTo Keith Addison Handmade Projects |
Aquaculture for small farms
A pond on a small farm can mean much better all-round farm integration and greater overall production. Apart from their use for ducks and geese, ponds can raise a useful supply of fish.
Plant and animal wastes fertilise the pond and/or feed the fish, sludge from the pond fertilises the croplands to raise more plants and animal-feed.

(ICAAE)
Ponds are also useful for waterharvesting in dry areas, storing water as a resource for the farm while being used for fish-raising. And ponds are often a viable land-use for marginal land or poor land. Even a small pond in a backyard can be a worthwhile source of food.
Aquaculture resources
 "Small Scale Aquaculture: A Guide to Backyard Fish Farming" by Steven D. Van Gorder, 1992, Rodale Institute, ISBN 0-9677732-0-2
"Small Scale Aquaculture: A Guide to Backyard Fish Farming" by Steven D. Van Gorder, 1992, Rodale Institute, ISBN 0-9677732-0-2
Details and plans on how to raise, harvest, prepare, and store over 100lbs of fish in five months. This system is the result of eight years of research at the Rodale Research Center. A simple and efficient way to produce your own fish on a scale appropriate for a self-sustaining household. Makes home aquaculture as practical as gardening for providing healthy food for a family. Features an ecologically sound recirculating system designed for low energy and low water use made from readily available materials. From Rodale Institute Bookstore:
http://www.rodaleinstitutestore.org/store/customer/
product.php?productid=910&cat=354&page=1
Water Harvesting and Aquaculture for Rural Development Series from the International Center for Aquaculture and Aquatic Environments (ICAAE), Department of Fisheries and Allied Aquacultures, Auburn University, Alabama. The ICAAE has worked on development in 97 countries. This is a useful series of 20 online booklets, clear and well-illustrated. Aquaculture, ponds, fertilization, feeding, tilapia, polyculture, rice paddies, intensive cage culture, water harvesting, more.
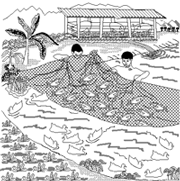
From "An Introduction to Aquaculture"
http://www.ag.auburn.edu/fish/international/
waterharvestingpubs.php
ICAAE home page:
http://www.ag.auburn.edu/fish/international/
FAO illustrated guides online
Freshwater Fish Farming: How to Begin -- Better Farming Series 27 (FAO, 1979, 43 pp) -- What is fish farming?, Why do we raise fish?, What do you need to raise fish?, How do we begin?, The pond, Where to put your fish pond, Compost to fertilize your pond, How to dig your pond, The water, Filling your pond, Fertilizing the water in the pond, How to make compost, Putting the fish into your pond, Feeding your fish, Taking care of your pond, Harvesting your fish, What to do with your baby fish, What to do with your big fish, Now you must begin again... Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/fish/fb27fe/en/b92.htm
Freshwater Fish Farming: the Pond -- Better Farming Series 29 (FAO, 1981, 43 pp) -- Improving your fish, Planning a bigger pond, Where to put your pond, Water, Place, Soil, Testing soil, How large should your pond be? Building a bigger pond, How to make your old pond bigger, How to build a new, bigger pond, The inlet, The outlet, A better outlet, The overflow, A siphon, Screens. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/
cd3wd/fish/fb29fe/en/b94.htm
Better Freshwater Fish Farming: the Fish -- Better Farming Series 30 (FAO, 1981, 48 pp) -- Filling your pond with water, Fertilizing the water in your pond, Putting fertilizer into the crib, When is your pond ready?, Taking care of your pond, The fish, Growing your own baby fish, Feeding the fish in your nursery pond, Moving your baby fish, Carrying your baby fish, Putting baby fish into your big pond, Feeding your big fish, Taking care of your fish, Harvesting your fish, Harvest without draining the water, Harvest by draining all of the water, Harvest by draining part of the water, What to do with your big fish, What to do with your baby fish, Now you must begin again... Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/fish/fb30be/en/b95.htm
Better Freshwater Fish Farming: Further Improvement -- Better Farming Series 35 (FAO, 1986, 61 pp) -- Ways to improve, The ponds, Building even bigger ponds or more ponds, A nursery pond, Filling and emptying smaller ponds, Filling and emptying bigger ponds, Bringing water to your ponds, Raising the level of your water supply, Digging a supply ditch, Digging a return ditch, Controlling the water in your supply ditch, Filling your ponds, How to fill your ponds, Better fertilizing, The fish, Growing fish all year round, Growing only male fish, Harvesting your fish, Harvesting many fish, Harvesting fish when you have a monk, Your farm and your fishponds, Your fishponds and your health. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/agric/fb35be/en/b100.htm
Better Freshwater Fish Farming: Raising Fish in Pens and Cages -- Better Farming Series 38 (FAO, 1990, 83 pp) -- Raising fish in pens and cages, The baby fish, Pens, Building a pen, Carrying small fish, Putting baby fish into your pen, Feeding fish in pens, Taking care of the fish and pen, Harvesting fish in pens, Now you must begin again, Raising your own baby fish in pens, Cages, Building a cage, Carrying small fish, Putting baby fish into your cage, Feeding fish in cages, Taking care of the fish and cage, Harvesting fish in cages, Now you must begin again, Raising your own baby fish in cages. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/cd3wd/fish/fb38be/en/b103.htm
 "On-Farm Fish Culture", Agrodok No. 21, 1998, Agromisa Foundation -- Crops or animal husbandry can easily be integrated with fish culture, with total production higher and more efficient than farms which haven't been integrated. Step by step strategy: principles of integrated fish culture and the use of plant material as fish feed and/or fertilizer, factors influencing the biological system in a fish pond, integration of fish culture with rice culture or several kinds of livestock production (pigs, poultry, ducks and geese, other livestock), many examples of possible combinations, by-products use, animal manure, using slurry from the pond as fertilizer for crops. Download pdf here.
"On-Farm Fish Culture", Agrodok No. 21, 1998, Agromisa Foundation -- Crops or animal husbandry can easily be integrated with fish culture, with total production higher and more efficient than farms which haven't been integrated. Step by step strategy: principles of integrated fish culture and the use of plant material as fish feed and/or fertilizer, factors influencing the biological system in a fish pond, integration of fish culture with rice culture or several kinds of livestock production (pigs, poultry, ducks and geese, other livestock), many examples of possible combinations, by-products use, animal manure, using slurry from the pond as fertilizer for crops. Download pdf here.
"Small-Scale Freshwater Fish Farming", Agrodok No. 15, 1996, Agromisa Foundation -- Basic information for beginners. Principles of fish farming, site selection and choice of fish farm type. Detailed description of how to set up a small-scale fish farm for subsistence to provide daily protein requirements. Fish farming practises, choice of species, nutrition, health, reproduction, harvesting. Pond construction (appendix) and maintenance. Focus is on carp, tilapia, catfish. Download pdf here.
Freshwater Fish Pond Culture and Management by Marilyn Chakroff, VITA (Volunteers in Technical Assistance) -- A comprehensive guide to planning, constructing, and maintaining small- scale warm water fish and pond operations. A valuable reference manual. Fully illustrated. 196pp. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/vita/fishpond/en/fishpond.htm
Understanding Aquaculture by Ira J. Somerset, VITA (Volunteers in Technical Assistance) -- Discusses various methods of raising fish, shellfish, and molluscs for food and profit. 24pp. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/vita/aquacult/en/aquacult.htm
Understanding Fish Preservation and Processing by Richard T. Carruthers, VITA (Volunteers in Technical Assistance) -- Presents guidelines for preserving fish by means of salting, smoking, and pickling. 10pp. Full text free online at CD3WD 3rd World Development online library:
http://www.cd3wd.com/cd3wd_40/vita/fishproc/en/fishproc.htm
Roofwater Fish Farm Ideal For Learning -- Australian Vivienne Hallman is proving that urban fringe farmers can grow native fish successfully on natural foods. Most of the water can come from a home rooftop. Much of the fish food can be home-grown earthworms and insect larvae. Vivienne's project has shown how Australian native fish could be reared in a small area on worm-farmed kitchen scraps -- to give benefits to a vegetable or fruit tree garden. "One crop a year of silver perch is possible with unheated water," she said. Up to 50 fish a year can be raised in a 4,000-litre [900 gallons], unheated tank, to 350 to 400 gram size [about 1-lb]. "This means each of my five tanks is capable of raising 17 to 20 kg [37-44 lb] of silver perch under the non-stressful growing conditions I favour," Vivienne said. http://www.cityfarmer.org/fishfarm.html
"Raising catfish in a barrel" -- A biological food chain in the back yard produces fresh fish for the table and compost for the garden, by Philip and Joyce Mahan, from Organic Gardening and Farming, November, 1973. Download pdf here.
 Chinese Methods for Integrating Fish Culture with Crop and Livestock Farming -- Integration of fish, livestock, and crop production in China has been refined over 2,000 years. The system recycles resources, reduces organic pollution (livestock and poultry manure are good organic fertilizers for fish farming), and combines fish farming with mulberry cultivation for raising silkworms. The silkworm pupae are used as fish feed, and the worm faeces and wastewater from silk processing as pond fertilizers. Pond silt is used as fertilizer for fodder crops, which can in turn be used to feed livestock, poultry, and fish. Online paper:
Chinese Methods for Integrating Fish Culture with Crop and Livestock Farming -- Integration of fish, livestock, and crop production in China has been refined over 2,000 years. The system recycles resources, reduces organic pollution (livestock and poultry manure are good organic fertilizers for fish farming), and combines fish farming with mulberry cultivation for raising silkworms. The silkworm pupae are used as fish feed, and the worm faeces and wastewater from silk processing as pond fertilizers. Pond silt is used as fertilizer for fodder crops, which can in turn be used to feed livestock, poultry, and fish. Online paper:
http://archive.idrc.ca/nayudamma/fishcul_30e.html
 "Rice-Fish Culture in China" edited by Kenneth T. MacKay, IDRC, 1995, 240 pp, ISBN 0-88936-776-0, $35
"Rice-Fish Culture in China" edited by Kenneth T. MacKay, IDRC, 1995, 240 pp, ISBN 0-88936-776-0, $35
Raising fish in rice paddies brings to farmers in Asia an important source of protein, as well as extra income. Biological and ecological aspects of rice-fish culture, and the economic and social dimensions. Full text free online:
http://www.idrc.ca/en/ev-9299-201-1-
DO_TOPIC.html
 "Duckweed -- a potential high-protein feed resource for domestic animals and fish", by R.A. Leng, J.H. Stambolie and R. Bell, Centre for Duckweed Research & Development University of New England Armidale, NSW Australia, Livestock Research for Rural Development, Volume 7, Number 1, October 1995 -- "... duckweeds yield 10-30 ton DM/ha/year (dry matter per hectare per year) containing up to 43% crude protein, 5% lipids and a highly digestible dry matter. Duckweeds have been fed to animals and fish to complement diets, largely to provide a protein of high biological value. Fish production can be stimulated by feeding duckweed to the extent that yields can be increased from a few hundred kilograms per hectare/year to 10 tonnes/ha/year." Online paper:
"Duckweed -- a potential high-protein feed resource for domestic animals and fish", by R.A. Leng, J.H. Stambolie and R. Bell, Centre for Duckweed Research & Development University of New England Armidale, NSW Australia, Livestock Research for Rural Development, Volume 7, Number 1, October 1995 -- "... duckweeds yield 10-30 ton DM/ha/year (dry matter per hectare per year) containing up to 43% crude protein, 5% lipids and a highly digestible dry matter. Duckweeds have been fed to animals and fish to complement diets, largely to provide a protein of high biological value. Fish production can be stimulated by feeding duckweed to the extent that yields can be increased from a few hundred kilograms per hectare/year to 10 tonnes/ha/year." Online paper:
http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd7/1/3.htm
The Integrated Tilapia & Duckweed Farming System -- The fish and the waters of the tilapia growout ponds provide the nutrients upon which the duckweed will thrive. In turn, the duckweed removes unwanted nutrients and waste products from the system, converting the nutrients into plant biomass. This plant biomass, in turn, becomes a high protein food for the tilapias. While all this is going on, water within the integrated system is conserved and purified. The entire system is a natural and sustainable approach to aquaculture.
http://www.fishfarming.com/recirc.html
Duckweed Aquaculture -- A New Aquatic Farming System for Developing Countries, Paul Skillicorn, William Spira & William Journey, (1993) The World Bank -- "The PRISM Group initiated a pilot project in Bangladesh to develop farming systems for duckweed and to test its value as a fish feed. The results of the pilot operations were extremely promising; production of duckweed-fed carp far exceeded expectations, and dried duckweed meal provided an excellent substitute for soy and fish meals in poultry feeds. Duckweed could be grown using wastewater for nutrients, or alternatively using commercial fertilizers. Duckweed-fed fish production does not depend on mechanical aeration and appears to be significantly more productive and easier to manage than traditional pond fish culture processes." Download pdf:
http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/
WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/1993/03/01/000009265_3970128103342/
Rendered/PDF/multi_page.pdf
AquaNIC Aquaculture Network Information Center is intended to be a gateway to electronic resources in aquaculture. Maintained at Purdue University and supported by the US Department of Agriculture Extension Service. Searchable database, plus centralized search of a variety of other databases. Useful resources for beginners and discussion groups, categorized by Species and by Systems.
http://aquanic.org/
Fishing for Information -- links to Internet resources on aquaculture, fisheries, fish farming, shrimp, water resources, etc, from the Institute of Aquaculture at Stirling University in Scotland.
http://www.fishing4info.com/
The FishBase Global Information System on Fishes was developed at the International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management (ICLARM) in collaboration with the FAO. Web-based searchable information and pictures on over 20,000 fresh and saltwater fish. Common name, scientific name, location, biology, culture, references, more 30,200 species, 265,200 common names, 45,700 pictures, 41,100 references).
http://www.fishbase.org/
FishBase Book:
http://www.fishbase.org/manual/English/contents.htm
Massive Fish FAQ from the Northeast Fisheries Science Center -- plus a page of other fish FAQs. Do fish sleep? Do they chew their food? Everything about fish, as well as lobsters, shrimp, crabs, whales, turtles, porpoises, clams.
http://www.wh.whoi.edu/faq/index.html
Small farms
Small farm resources
Community-supported farms
Farming with trees
Farming with animals
Pasture
Pigs for small farms
Poultry for small farms
Aquaculture for small farms
Composting for small farms
Controlling weeds and pests
Small farms library
City farms
Organic gardening
Building a square foot garden
Plant spacing guides
No ground? Use containers
When to sow what
Seeds
Garden pond
Gardening resources
Composting
Making compost
Composting resources
Composting indoors
Vermicomposting
Humanure
Composting for small farms