
![]()
Search the Journey to Forever website – click HERE
|
Journey to Forever: Make a donation |
En español
Biocombustibles, biodiesel
Navigation
Contact usTo Keith Addison Handmade Projects |
Why quality matters
Spanish version -- Versión en español
They conducted field trials with biodiesel in collaboration with end-users and found the following injection equipment and engine problems: This is what caused problems: Corrosive acids (formic & acetic)
The Fuel Injection Equipment (FIE) Manufacturers (Delphi, Stanadyne, Denso, Bosch) issued a statement on biodiesel. They strongly support it, but they have their concerns too, and they're very involved in standards development. They had a fright in Europe in the early 90s when the introduction of low-sulfur diesel saw widespread damage to injection systems, with excessive wear and failure. The same thing happened in California. They don't want it to happen with biodiesel. These are their concerns:
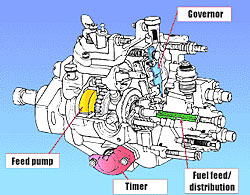
Denso Distributor Injection Pump
Free methanol in biodiesel
Effect: Corrodes aluminium & zinc, Low flash point
Failure Mode: Corrosion of fuel injection equipment
Biodiesel process chemicals
Effect: Potassium and sodium compounds, Solid particles
Failure Mode: Blocked Nozzles
Dissolved water in biodiesel
Effect: Reversion of biodiesel to fatty acid
Failure Mode: Filter Plugging
Free water in mixtures
Effect: Corrosion, Sustains bacteria, Increases the electrical conductivity of fuel
Failure Mode: Sludging, Corrosion of fuel injection equipment
Free glycerine, Mono-& di-glyceride
Effect: Corrodes non-ferrous metals, Soaks cellulose filters, Sediments on moving parts and Lacquering
Failure Mode: Filter clogging, Injector Coking
Free fatty acid
Effect: Provides an electrolyte and hastens the corrosion of zinc, Salts of organic acids, Organic compounds formed
Failure Mode: Corrosion of fuel injection equipment, Filter plugging, Sediments on parts
Higher modulus of elasticity
Effect: Increases injection pressure
Failure Mode: Potential of reduced service life
High viscosity at low temperature
Effect: Generates excessive heat locally in rotary distributor pumps, Higher stressed components
Failure Mode: Pump seizures, Early life failures, Poor nozzle sprayAgeing products
Effect: Corrodes all metallic parts
Failure Mode: Corrosion of fuel injection equipment
Higher molecular organic acids
Effect: Similar to fatty acid
Failure Mode: Similar to fatty acid
Polymerisation products
Effect: Deposits especially from fuel mixes
Failure Mode: Filter plugging, Lacquering formation in hot areas
FIEM statement in full -- Acrobat file, 104kb
Engine manufacturers have similar concerns, especially with the oxidation of biodiesel leading to a gradual increase in contamination and free water content.
The final US ASTM specification D6751 for biodiesel is based on the existing petro-diesel standard, D975, which was modified by elimination of items not applicable to biodiesel and by addition of items specific to biodiesel. A lot of work went into developing new analytical methods for a number of biodiesel properties. It's based on the hard realities of what bad fuel does to motors and fuel systems.
The German draft standard DIN EN 14214, "Automotive fuels - Fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) for diesel engines - Requirements and test methods", is one of the most complete biodiesel specifications.
The EU CEN technical committee TC19 is evolving European Standards and is liaising with the International Standards Organisation committee TC28 regarding an eventual world-wide standard.
They're not just bumbling around. There's a huge increase in diesel use, very rapid advances in diesel technology, stringent requirements in improving diesel emissions, tremendous growth in biodiesel production. They're dealing with billions and billions of dollars, with entire transport systems.
We homebrewers can do whatever we like, but it's quite possible for a homebrewer to make standard-spec fuel, in fact it's easy, so why not do it?
-- Keith Addison, message to the Biofuel mailing list, December 11, 2002 -- with thanks to DieselNet/Ecopoint Inc.
http://www.dieselnet.com/
See: National standards for biodiesel
Back to:
Biodiesel and your vehicle
Biofuels
En español -- Biocombustibles, biodiesel
Biofuels Library
Biofuels supplies and suppliers
Biodiesel
Make your own biodiesel
Mike Pelly's recipe
Two-stage biodiesel process
FOOLPROOF biodiesel process
Biodiesel processors
Biodiesel in Hong Kong
Nitrogen Oxide emissions
Glycerine
Biodiesel resources on the Web
Do diesels have a future?
Vegetable oil yields and characteristics
Washing
Biodiesel and your vehicle
Food or fuel?
Straight vegetable oil as diesel fuel
Ethanol
Ethanol resources on the Web
Is ethanol energy-efficient?